- Origin: Persian رستم
- Meaning: unknown
- Gender: Male
Rostam is an ancient Persian name that likely descends from Old Persian or Sogdian roots. Its meaning is debated, but the most popular theory is that it derives from *rautas-taxma “strong like a river.”
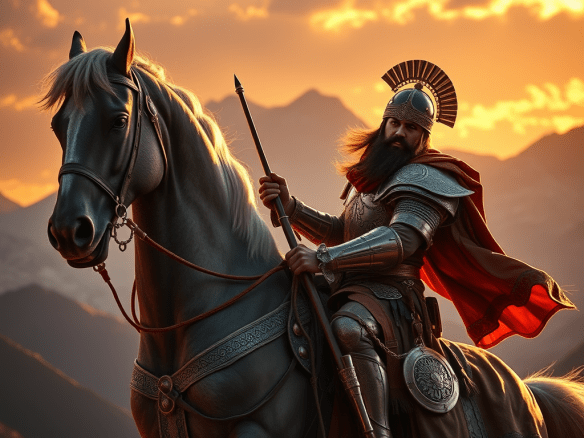
The name is immortalized in Ferdowsi’s 10th-century Persian epic, the Shahnameh, where Rostam is the towering national hero described as:
- a mighty warrior of the kingdom of Zabul.
- tamer of the legendary horse Rakhsh.
- defender of Iran against its enemies
- and the tragic father of Sohrab in one of the most famous father-son duels in world literature.
Because of this epic, Rostam is to Persian culture what Hercules is to the Greek tradition.
Rostam has been a popular masculine name across Iran, Afghanistan, Tajikistan, and Central Asia for over a thousand years. It also appears as Rustam in many languages of the region—Azerbaijani, Uzbek, Pashto, and even in parts of the Caucasus and South Asia.
International Variations
- Rüstəm (Azeri)
- Rustam Рустам, رستم (Chechen, Kazakh, Kyrgyz, Indonesian, Pashto, Tajik, Urdu, Uyghur, Uzbek)
- Rostom როსტომ (Georgian)
- Rustem Рустем (Russian)
- Rustan, Rusten (Scandinavian)
- Röstäm Рөстәм (Tatar)
- Rüstem (Turkish)
Sources







